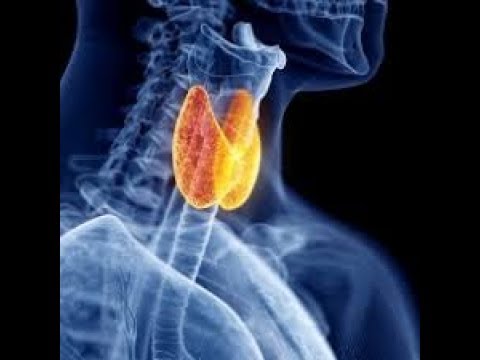
Donde Queda La Tiroides: Understanding the Thyroid’s Location and Function
The question “Donde Queda La Tiroides?” translates to “Where is the thyroid?” in English. Understanding the thyroid’s location is crucial to appreciating its role in overall health. This small, butterfly-shaped gland, nestled in the front of your neck, plays a vital role in regulating metabolism and energy levels. This article delves into the precise location of the thyroid, its function, potential issues, and how to maintain its health. Knowing exactly donde queda la tiroides is just the first step toward better health awareness.
Anatomical Location of the Thyroid
So, donde queda la tiroides specifically? The thyroid gland is located in the anterior (front) part of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple (laryngeal prominence). It sits against and wraps around the trachea (windpipe). Its butterfly shape is formed by two lobes, one on each side of the trachea, connected by a narrow band of tissue called the isthmus. This isthmus crosses the trachea usually at the level of the second to fourth tracheal rings.
To be more precise, the thyroid is situated between the cricoid cartilage (a ring of cartilage forming the lower part of the larynx) above and the suprasternal notch (the dip in the middle of the collarbone) below. The common carotid arteries, major blood vessels supplying the head and neck, run alongside the thyroid lobes. Understanding donde queda la tiroides is essential for medical professionals during examinations and procedures.
The Thyroid’s Vital Function
Now that we know donde queda la tiroides, it’s important to understand what it does. The thyroid gland is a key player in the endocrine system, responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism. The primary hormones it secretes are thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones influence nearly every physiological process in the body, including heart rate, body temperature, and energy expenditure. The thyroid’s function is tightly controlled by the pituitary gland, which releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH signals the thyroid to produce T3 and T4.
These hormones affect growth and development. Therefore, understanding donde queda la tiroides and its function becomes particularly important in children and adolescents.
Common Thyroid Disorders
Several conditions can affect the thyroid gland, disrupting its normal function. These include:
- Hypothyroidism: This occurs when the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones. Symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, constipation, and depression.
- Hyperthyroidism: This condition results from an overactive thyroid, leading to excessive hormone production. Symptoms include weight loss, anxiety, rapid heartbeat, and tremors.
- Goiter: An enlargement of the thyroid gland, often caused by iodine deficiency or other underlying conditions.
- Thyroid Nodules: Lumps that can develop within the thyroid gland. Most nodules are benign, but some may be cancerous.
- Thyroid Cancer: A relatively rare cancer that originates in the thyroid gland.
Knowing donde queda la tiroides allows for more accurate diagnosis of these conditions through physical examination and imaging techniques.
Diagnosing Thyroid Problems
Diagnosing thyroid disorders typically involves a combination of physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies. Blood tests measure TSH, T4, and T3 levels to assess thyroid function. Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound, can help visualize the thyroid gland and detect any abnormalities. Fine needle aspiration biopsies may be performed to evaluate thyroid nodules for cancer.
Since we understand donde queda la tiroides, doctors can easily perform palpation during physical examination to check for any enlargement or nodules.
Maintaining Thyroid Health
While some thyroid conditions are unavoidable, there are steps you can take to support thyroid health:
- Ensure adequate iodine intake: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production. Consume iodized salt or foods rich in iodine, such as seaweed and seafood.
- Avoid excessive iodine intake: While iodine deficiency can cause problems, too much iodine can also be harmful. Follow recommended daily intake guidelines.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can disrupt hormone balance and negatively impact thyroid function. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Limit exposure to environmental toxins: Certain environmental toxins, such as perchlorate and pesticides, can interfere with thyroid hormone production.
- Get regular checkups: If you have a family history of thyroid disease or experience symptoms suggestive of thyroid dysfunction, see your doctor for regular checkups.
Understanding donde queda la tiroides and its importance encourages proactive health management.
The Thyroid and Pregnancy
Thyroid function is particularly important during pregnancy. Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in fetal brain development. Untreated thyroid disorders during pregnancy can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby. Pregnant women should undergo thyroid screening, especially if they have a history of thyroid disease or symptoms suggestive of thyroid dysfunction. Medication can be prescribed to ensure proper levels of thyroid hormones are maintained throughout the pregnancy.
Donde queda la tiroides is a common question for pregnant women, as they are often advised to monitor their thyroid health closely.
The Thyroid and Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, are common causes of thyroid disorders. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition that attacks the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism. Graves’ disease is an autoimmune condition that stimulates the thyroid gland, leading to hyperthyroidism. These conditions require careful management by a healthcare professional.
Understanding donde queda la tiroides doesn’t directly impact treatment of autoimmune conditions but helps in understanding the target organ of these diseases.
Thyroid Medication and Treatment
Treatment for thyroid disorders depends on the specific condition and its severity. Hypothyroidism is typically treated with levothyroxine, a synthetic thyroid hormone that replaces the hormones the thyroid is not producing. Hyperthyroidism may be treated with antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine, or surgery. Thyroid nodules may be monitored or removed surgically if they are cancerous or causing symptoms.
Knowing donde queda la tiroides helps surgeons accurately target the gland during surgical procedures. [See also: Thyroidectomy Recovery Tips]
The Role of Diet and Nutrition
Diet and nutrition play a supporting role in thyroid health. Certain nutrients, such as selenium and zinc, are important for thyroid hormone production and function. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support overall thyroid health. However, it’s important to note that diet alone cannot cure thyroid disorders. Medical treatment is often necessary.
While diet isn’t a primary treatment, understanding donde queda la tiroides and its function reinforces the importance of a healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion
Understanding donde queda la tiroides – where the thyroid is located – is the starting point for understanding its crucial role in regulating metabolism and overall health. This small gland, situated in the front of the neck, produces hormones that affect nearly every organ system in the body. By understanding the thyroid’s function, potential disorders, and ways to maintain its health, you can take proactive steps to support your well-being. If you have concerns about your thyroid health, consult with a healthcare professional for evaluation and management. Prioritizing thyroid health contributes significantly to a healthier and more energetic life. Now that you know donde queda la tiroides, you can be more informed about your health.
